
Delving operating cycle formula into the mechanics of business efficiency, calculating the operating cycle emerges as a pivotal task for financial managers aiming to optimize cash flow and enhance resource management. Overall, the importance of calculating the operating cycle cannot be overstated. Effective integration between accounting and inventory management software ensures seamless data flow and allows you to make informed decisions to optimize your operating cycle. A low DSI suggests that your company is efficiently managing inventory and selling products quickly.
- Integration between these tools can enhance your ability to manage and optimize your operating cycle effectively.
- The operating cycle in working capital is an indicator of the efficiency in the management.
- This allows businesses to identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement, ultimately leading to a more streamlined and profitable operation.
- It indicates that a business converts inventory and receivables into cash more quickly, improving liquidity and reducing the need for external financing.
- On the downside, a short cycle could mean the company is losing out on opportunities to use credit terms for its benefit.
- Days inventories outstanding equals the average number of days in which a company sells its inventory.
Key Takeaway:
They subtract accounts payable time by the net operating cycle, which causes a variance between the two calculations. The company is able to accomplish it since the net operating cycle only cares about the period from when an inventory is purchased to when they receive money from the sales of stock. A high DPO suggests that your company is effectively managing its accounts payable, optimizing cash flow by extending payment terms without straining supplier relationships. This can be particularly beneficial for businesses looking to reduce working capital requirements and enhance profitability. Days Sales Outstanding (DSO) measures the average number of days it takes for your company to collect payments from customers after making a sale.
Examples of Operating Cycles
One crucial aspect of business operations that can impact both job seekers and employers is the concept of an operating cycle. Since there are no credit sales, time taken in recovering cash from accounts receivable is zero. The Operating net cycle (NOC) refers to the period between paying for inventory and cash collected through the sale of receivables. In contrast, an operating cycle assesses the effectiveness of the operations, yet they are both beneficial and offer essential knowledge. An operating cycle is one more valuable tool in the toolkit of financial analysis that helps businesses make wiser, more informed decisions.
Example 1: Retail Industry
A negative operating cycle occurs when a company’s accounts payable (DPO) period is longer than the combined inventory days and days sales outstanding (DSO) periods. This situation is rare and indicates that the company can collect cash from customers before paying suppliers, resulting in a source of cash flow. Efficient management of the operating cycle is crucial for businesses to improve cash flow, optimize resources, and enhance overall productivity. By understanding the components of the operating cycle and how to calculate it, companies can make informed decisions that positively impact their financial health.

E-Commerce Financial Model Template

The quicker a business makes money, the more capable it will be of paying off any obligations due or growing as necessary. The operating cycle formula in financial management helps determine the time a business takes to purchase inventory, then sell the inventory and then collect the cash from the sale of the inventory. Using the equation to calculate the operating cycle enables the management of a firm be aware of the cash flow in and out of their business.
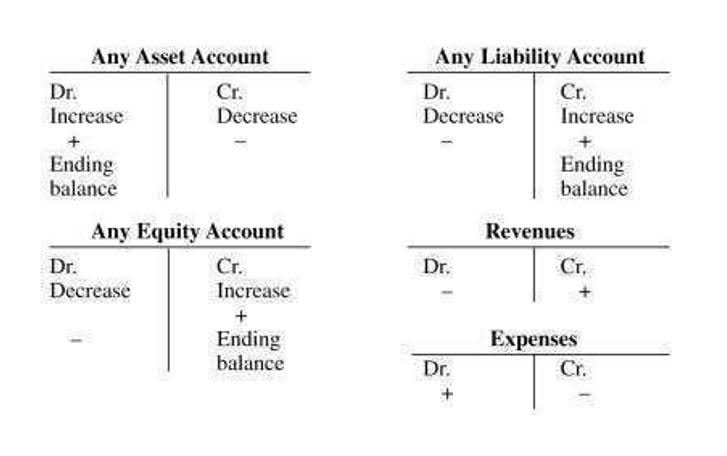
- The Operating Cycle is calculated by getting the sum of the inventory period and accounts receivable period.
- Understanding the components of an operating cycle is crucial for both job seekers and employers in today’s competitive market.
- When evaluating potential employers, candidates can inquire about the company’s operating cycle to gain insights into its financial stability and efficiency.
- In parallel to receiving payments from customers, companies also have to manage accounts payable.
- When there is a significant different between current ratio and quick ratio, it is useful to study the operating cycle and cash conversion cycle to ascertain whether the company’s funds are less-profitable assets.
- Understanding and managing your operating cycle is fundamental to your business’s financial health.
- One of the best examples of a company with the ideal operational efficiency is Toyota.
The operating cycle is a financial metric that measures the time it takes for a company to convert its investments in inventory and accounts receivable into cash. Essentially, it is the duration between the acquisition of inventory and the collection of cash from customers after selling the inventory. In a competitive job market, what are retained earnings understanding and efficiently managing your company’s operating cycle is crucial for maintaining financial health and success. Let’s delve into a real-life example to demonstrate how calculating the operating cycle can provide valuable insights for businesses. A related concept is that of net operating cycle which is also called the cash conversion cycle.
We may earn a commission when you click on a link or make a purchase through the links on our site. All of our content is based on objective analysis, and the opinions are our own. They also make large quantities of these items and have little to no inventory to maintain. For example, take a look at retailers like Wal-Mart and Costco, which can turn their entire inventory over nearly five times during the year.
HighRadius seamlessly integrates with Bookkeeping for Chiropractors leading ERPs like SAP and Oracle, ensuring a smooth and comprehensive O2C process. This integration allows businesses to leverage existing systems and data, significantly enhancing overall efficiency and accuracy. Good management means a company can pay bills on time without borrowing too much. It reflects not just on liquidity but also a company’s agility in managing resources, which can be pivotal for strategic decision-making and competitive advantage. This means that companies can reduce or eliminate slow-moving or obsolete inventory, which in turn reduces the cost and time needed to dispose of these items.
This means it takes the company about 102.2 days to convert its inventory into cash through sales and collections. On the other hand, a longer business operating cycle can strain cash flow, as money is tied up in inventory and receivables for an extended period. This can lead to cash shortages, making it challenging to pay bills, cover operating expenses, or seize new opportunities. A shorter operating cycle might suggest a company’s efficiency in managing its inventory and receivables, while a longer one could imply delays or slower turnover. Managing the operating cycle affects how much money a business has for daily use. A company with a quick operating cycle will need less cash on hand because it turns products into cash faster.





